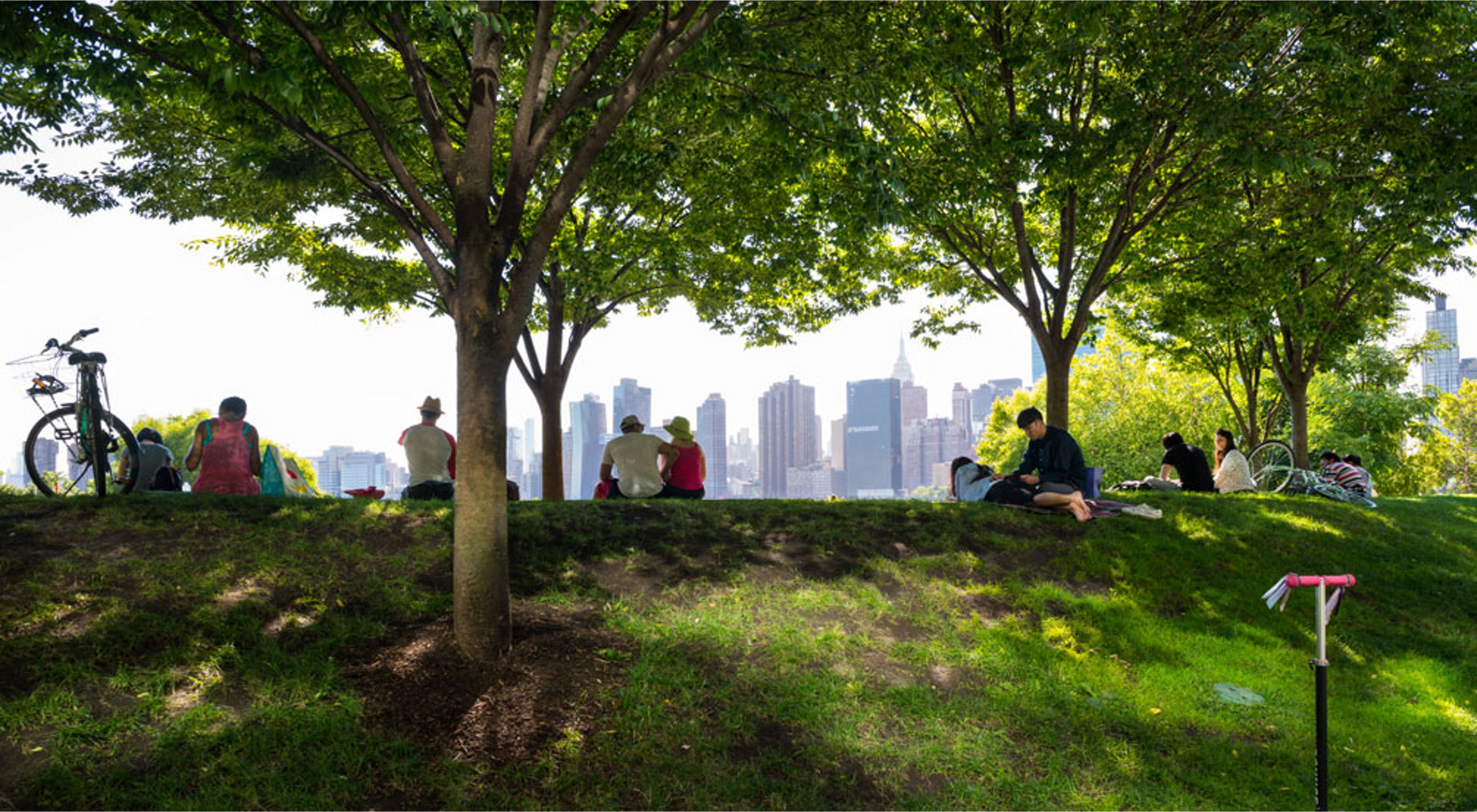
Trees, often anointed to the lungs of the Earth, play a paramount role in maintaining a sustainable environment. Their considerable benefits extend beyond their aesthetic appeal, furnishing diverse ecological, economic, and social advantages. We will investigate how trees contribute to a sustainable environment, from carbon sequestration and habitat creation to enhancing air and water quality.
Ways trees contribute to a sustainable environment
- Carbon Sequestration
One of the trees’ most well-comprehended and paramount contributions to a sustainable environment is their ability to sequester carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Trees absorb CO2 and convert it into oxygen and glucose through photosynthesis, storing carbon in their tissues. This helps lessen the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigates climate change. As global concerns about climate change intensify, the role of trees in sequestering carbon becomes increasingly paramount. Forests, in particular, act as valuable carbon sinks, absorbing large quantities of CO2 and helping to stabilize the Earth’s climate. Reforestation and afforestation efforts, which implicate planting trees in areas previously devoid of forest cover, are paramount strategies for enhancing carbon sequestration.
2. Habitat Creation
Trees provide vital habitats for countless species of animals, birds, insects, and plants. From towering canopy trees to understory shrubs, diverse tree species create microenvironments supporting a wide biodiversity range. Forests, in particular, are biodiversity hotspots, serving as homes and breeding grounds for countless species. Conserving and protecting these habitats is essential for maintaining the balance of ecosystems. As forests and other tree-rich areas are preserved, species can thrive, and the interconnectedness of ecosystems is preserved. This contributes to the sustainability of the environment by preserving the web of life on which we all depend.
3. Air Quality Improvement
Trees are paramount in enhancing air quality in urban and rural environments. They serve as natural air filters, trapping particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides on their leaves and bark. Trees help reduce the adverse health effects of air pollution on humans and ecosystems by sponging and neutralizing these pollutants. Trees can enormously lessen the “urban heat island” effect in urban areas, where cities experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. Trees provide shade and release water vapor through transpiration, cooling the surrounding environment and making cities more livable.
4. Soil Protection and Nutrient Cycling
The root systems of trees help stabilize soil, preventing erosion and landslides. The roots also contribute to nutrient cycling by absorbing essential nutrients from the soil and making them available to other plants. This process helps maintain healthy soil and supports agricultural productivity. Additionally, trees’ fallen leaves, branches, and twigs provide organic matter to the soil as they decompose, enriching it with nutrients and enhancing soil structure. Healthy soils are crucial for growing crops and sustaining ecosystems, making trees indispensable contributors to sustainable land use.
5. Water Quality and Management
Trees play a vital role in maintaining water quality and managing water resources. Their root systems help to absorb excess rainfall and reduce surface runoff, which can lead to soil erosion and water pollution. This natural water management function is particularly valuable in stemming floods and maintaining stable water supplies. Furthermore, the shade trees provide helps keep water temperatures in streams and rivers cooler, which is crucial for aquatic habitats. Trees also contribute to groundwater recharge, ensuring a sustainable supply of freshwater. Sustainable forestry practices that protect watersheds and riparian areas are essential for maintaining water quality and quantity.
6. Economic benefits
Trees have paramount economic value in addition to their environmental contributions. Sustainable forestry and the timber industry provide jobs and support local economies in many regions. Beyond timber, trees contribute to the economy through non-timber forest products, such as fruits, nuts, and medicinal plants. Urban trees enhance property values and contribute to energy savings by providing shade and reducing heating and cooling costs. Additionally, the tourism industry often relies on tree-rich natural landscapes, attracting visitors and generating revenue for local communities.
Trees are integral to a sustainable environment, contributing to a wide array of ecological, economic, and social benefits. Their role in carbon sequestration, habitat creation, air quality improvement, soil protection, water management, economic prosperity, and human well-being cannot be overstated. As cities continue to grow, the incorporation of green infrastructure, such as parks, greenways, and urban forests, becomes increasingly important for enhancing the quality of life and ensuring the sustainability of urban areas. As we face growing environmental challenges such as climate change and habitat loss, preserving and planting trees is a key strategy for building a more sustainable future. Recognizing the importance of trees and taking proactive steps to protect and nurture them is a collective responsibility that will benefit current and future generations. When faced with the complex task of maintaining a thriving urban forest, many residents turn to professional tree services in Portland to ensure the health and longevity of their valuable trees.







Leave a Reply